Our bodies need vitamins to function at peak health and performance. They support important bodily functions. Vitamins also provide energy and help in cellular production as well as cell function. Not getting enough vitamins could lead to nutritional deficiencies and other dysfunctions. So, here’s a full guide to preventing and treating vitamin D deficiency.
One of the important vitamins you need to have is Vitamin D.
What Does Vitamin D do?
Vitamin D promotes strong and healthy bones and boosts energy levels. Your muscles, heart, lungs, and brain need this vitamin to function. It also helps different parts of your body fight infection.
There are natural ways to get Vitamin D – from sunlight, certain foods, and supplements. Your body processes Vitamin D from sunlight and supplements need to be changed by the body before it can be used. Your body then manages the calcium in your bones, gut, and blood thus helping the body properly communicate.
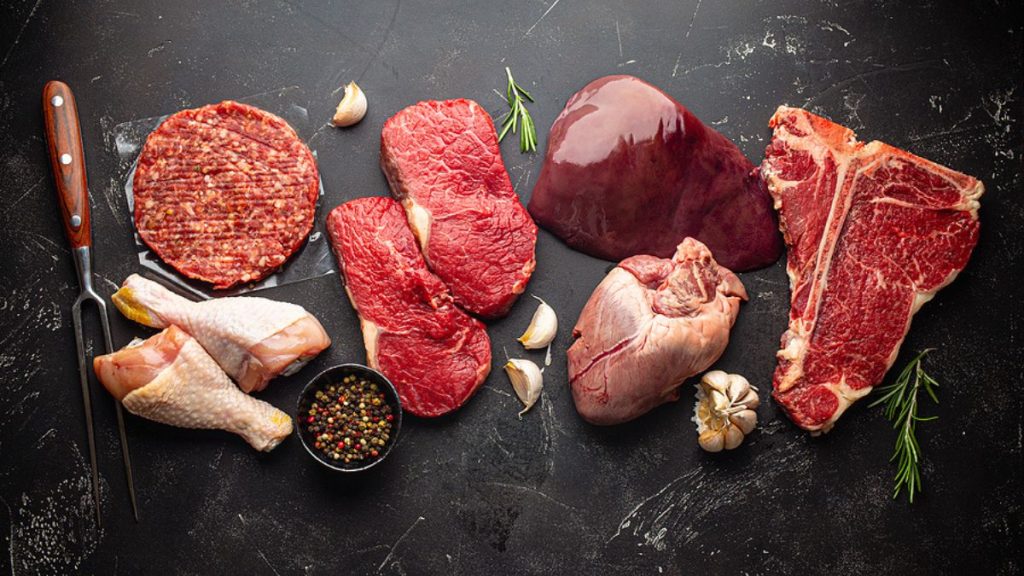
You can get Vitamin from the following foods:
- Cheese
- Egg Yolks
- Fatty Fish such as salmon, mackerel as well as tuna.
- Beef liver
- Fortified Vitamin D foods such as dairy products, orange juice, and soy milk.
Among these food choices, it’s been found that fish is the best source of Vitamin D.
When your body doesn’t have enough vitamin D, it may result in vitamin D deficiency.
What is Vitamin D Deficiency and Its Causes?
“What is vitamin D deficiency?” is a common question right next to “what is vitamin D” There are many reasons for having low vitamin D levels.
Here are some of them:
1. Lack of recommended vitamins over time.
If you follow a strict vegan diet, it’s easy to have Vitamin D deficiency. Most vitamin D foods are animal-based products like eggs, fortified milk, fish, etc. So when you don’t eat animal products, your risk of having vitamin D deficiency is higher.
2. Limited exposure to the sun
The body gets vitamin D from sunlight; our body uses it to create essential vitamins. When you limit your exposure to the sun, make sure to get vitamin D from other sources.
3. Dark skin
The darker your skin is, the harder it will be for your body to use the provided sunlight to process vitamin D. People with darker skin also face a higher risk of vitamin D deficiency, as they get older.
4. Kidney Problems
With most things, the older you become, the harder it gets for the body to perform at optimum levels. Your kidneys will have a difficult time converting vitamin D to its active form if you have kidney problems. This can easily lead to vitamin D deficiency.
5. Obesity
When you’re obese, vitamin D is extracted from the blood by the fat cells. This alters the release and circulation of the vitamin. People with body mass index higher than 30 are more likely to have lower levels of vitamin D.
6. Digestive Tract Issues
Some medical problems can affect other bodily functions. For example, Crohn’s disease, cystic fibrosis, and celiac disease cause the digestive tract to struggle to properly absorb vitamin D.
-
- Crohn’s disease makes it harder for you to digest gluten, which can often be found in bread and pasta. This affects how much nutrients your body absorbs. The symptoms of this disease include gas, bloating, fatigue and weight loss.
- Cystic fibrosis affects how the body produces sweat and mucus as well as how the lungs, digestive system, and other parts of your body work. An inherited defective gene is the cause of the disease.
- Celiac disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the digestive tract. Abdominal pain, diarrhea and weight loss are some of the symptoms of this disease.
What are Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms?
Now that you know what vitamin D deficiency is, the next step is to identify whether you are suffering from or at risk of having it. It’s important to note that the only way to be sure is to have a blood test but there are symptoms that may tell you that you are suffering from the deficiency.
Here are some of them:
1. Aching Bones
Many people who complain about aching bones are often thought to have chronic fatigue syndrome or fibromyalgia. However, it has been said that often, these symptoms are classic signs of vitamin D deficiency that leads to osteomalacia. This is different from the vitamin D deficiency that causes osteoporosis in adults. Vitamin D deficiency causes extra calcium to go into the collagen in your skeleton. This causes aching bones.
2. Feeling Blue
When you are exposed to bright light, the serotonin rises and then decreases with less exposure to the sun. Serotonin is a brain hormone that plays a part in your mood elevation. If you’re feeling blue, make an effort to go and enjoy the sun. In an experiment conducted in 80 elderly patients, researchers found that those with the lowest vitamin D levels were 11 times more likely to be depressed than those with healthy levels.
3. Gut trouble
If you have a gastrointestinal condition that causes you to have problems absorbing fat then you may have a lower chance of absorbing fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin D. This includes gut diseases like Crohn’s, inflammatory bowel disease, as well as celiac and non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
4. Head Sweating
A sweaty head is one of the first signs of a vitamin D deficiency according to studies. Many doctors actually ask new mothers if their baby’s head is sweating excessively for that very reason. If they are, it’s an early symptom of vitamin d deficiency and is caused by neuromuscular irritability.
If you have any of the symptoms we recommend contacting your doctor to book an appointment.
What are Your Risks When You Have Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D does so much more than make your bones strong, regulates the expression of genes that can influence your immunes system to fight infection, bacteria, and viruses and get rid of them. Vitamin D helps protect you against many things such as:
- Cardiovascular disease – this helps prevent strokes, heart attacks, heart disease, and hypertension.
- Autoimmune disease – Vitamin D prevents autoimmune diseases because it’s a potent immune modulator.
- Infections such as but not limited to influenza – Helps fight all kinds of infections.
- DNA repair and metabolic process – It’s been found to regulate genes and controls more or less 80 different metabolic processes this includes DNA repair as well as boosting the immune system and other biological processes.
What are Treatments for Vitamin D Deficiency?
So there are a few simple solutions: spend more time in the sun, eat more foods that are rich in vitamin D, or take supplements to increase your vitamin D levels.
Vitamin D3 is well regarded as the best choice in terms of supplements. How much vitamin D is needed to help correct your deficiency depends on the severity of your condition as well as your health risks. The time of the year also has a hand to play in this, if your blood is on low levels and it’s coming into winter, you’d need more time. Detecting the deficiency early is important so you can have more time to improve and maintain your levels.
Take supplements with meals that contain fat. It’s been shown that when consumed with a meal, especially one that contains fat, there’s a chance of an additional 32% vitamin D absorption. In certain studies, people were told to take the supplement with their biggest meal containing the most fat and in about three months they managed to get their levels right again. Consult your doctor to see what vitamin D supplementation guidelines he can suggest.
Vitamin D plays an important role in your body. Make sure that you are getting enough of the vitamin daily. If you are suffering from any Vitamin D deficiency symptoms, schedule a doctor’s appointment as soon as you can. The sooner you correct the deficiency, the lesser risks you have of developing vitamin D-related health conditions.

Rick Kaselj MS, is a leading kinesiologist and injury specialist as well as co-creator of the best-selling Unlock Your Hip Flexors program. Rick creates exercise programs that help people heal injuries and eliminate pain, so they can go back to living a full, active, healthy life.